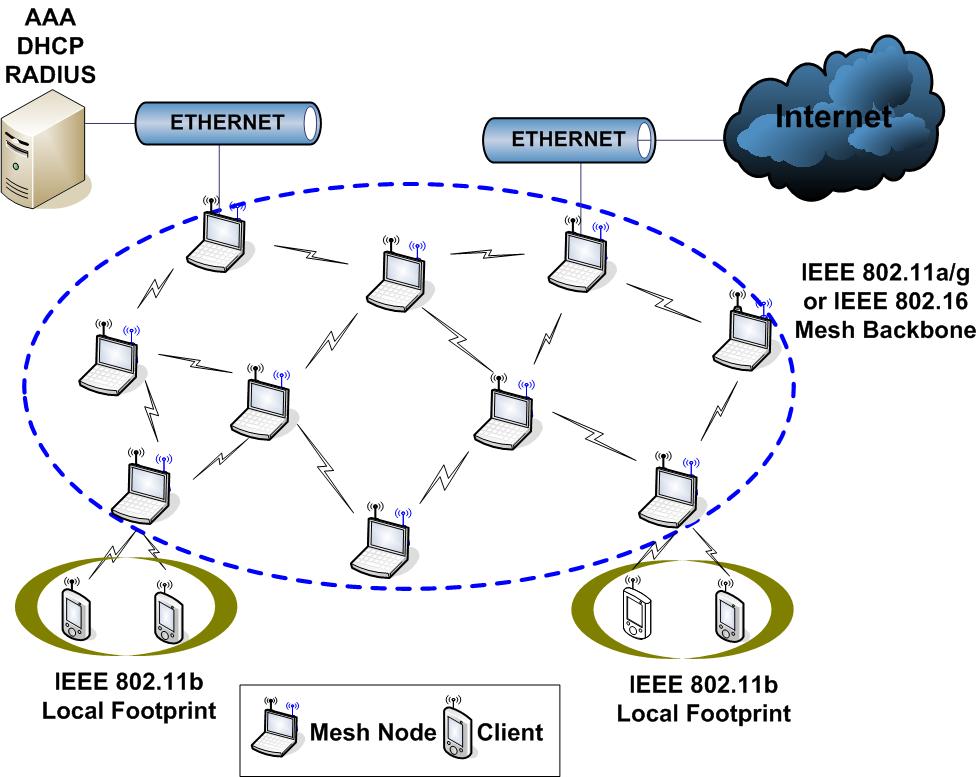
Mesh Networking
Author: Moffat Matenge
Last Modified: April 6, 2007
Mesh networking is a way to route data. It allows for continuous optimal connections and self maintainace to reconfigure communication channels in situations where a communication channel is unaccesible, expensive in terms of transmission time or congested .
The mesh network is based on an wireless ad-hoc concept and therefore requires the node hardware to be Wi-Fi or Wi-Max enabled and in the proximitity of hotspots. Mesh network protocol frameworks should be installed in all the participating nodes.
.
Contents |
How it works?
The core foundation of the network is based on graph theory and graph algorithms. The network is formed by an interconnected mesh of nodes equipped with a wireless interface-for example IEEE standards. Electromagnetic waves are used as communication channels. Information is passed from node to node using the most cost effective path. Intelligent self-reconfiguration also makes the entire mesh self-tuning end-to-end, allowing traffic to move dynamically along optimal paths. As those paths change, so too does the route table that directs traffic based on the shortest, fastest, least congested or other characteristic for each path. The self-configuring and self-tuning abilities contribute to the self-healing network characteristic. The multiple redundant paths add robust resiliency and, when properly arranged, eliminate single points of failure and potential bottlenecks within the mesh.Should any individual host become inaccessible or congested, alternate routes can be discovered and used providing a robust and reliable network topography.
Protocols
Many Mesh networks protocols and implementations are available. These protocols define a convention or standard that controls how nodes come to agree how to route packets between participating nodes.The protocols each have their own purpose and design principle. The following are some of the examples of the protocols available in to the industry, however this wiki page will not go much into details about the implementation and design of each protocol.
-
Mobile Mesh protocol which is made of three sub protocols responsible for: link discovery, routing and boarder discovery
-
GNU Zebra is free software that manages TCP/IP-based routing protocols.
-
AODV is a routing protocol for ad-hoc networks designed with mobile wireless enabled devices
Why is it gaining popularity?
The following sections will illustrate the advantages of mesh networks.
-
Cost: 802.11 enabled computing devices have become available at quite cheap prices. The fact that each mesh node runs both as a client and as a repeater potentially means saving.
-
Ease and simplicity: For a node to participate, it has to be pre-installed with wireless mesh software and uses standard wireless IEEE protocols such as 802.11b/g. Since routes are configured dynamically, joining the network is simply to drop the wireless enabled into the hotspot.
-
Organization and business models: In a mesh network, participating nodes maintain their own hardware, this minimizes the cost of setting up this network.
-
Network robustness: The mesh network has a self-healing mechanism, this allows for links to be dynamically reconfigured to optimize the path for routing.
-
Migration: Mesh networks allows for nodes to be mobile and still maintains reliable communication links.
Mesh networks have disadvantages, nevertheless, this disadvatages fall far from discouraging any interested person. The following are some of the drawback of setting up this network construct.
-
IP addresing issues: Nodes attempting to joining a mesh network tend to suffer from IP addressing allocation problem.
-
Hotspot proximity: A node attempting to join mesh networks needs to be in a neighbourhood of participating nodes. Hotspot are build in areas of node concentration
Examples
Below is a list of palces among many places that have implemented mesh networking:
See Also
- Wireless Ad-Hoc Network Intrusion Detection System
- Distributed communications through Bittorrent
- Speed of WiMax
- Onion Routing
External links
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mesh_network
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wireless_mesh_network
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mobile_ad-hoc_network
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/IEEE_802.11
References
Kevin Sornberger-css and html template