WiMax as Last Mile Solution
WiMax is a whole new technology offers the “last mile” solution. It is a
wireless metropolitan area network (MAN) technology covers up to 30 miles in
range theatrically. Each WiMax station can offer 75Mbits/s data rate to each of
its users.1 It provides business subscriber broadband connection similar to T1
and provides home users with mobile connection at the same speed as xDSL or
cable. The bandwidth is enough for 45 T1 lines or 25 home users with 3Mbps
bandwidth each. With multi-sector setup, there are WiMax products that supports
up to 6000 users yet able to provide each user with 10Mbps of bandwidth
available in the market .
WiMax Usage
There are many different areas that WiMax could be used to provide High Speed
Wireless Access.
Compare WiMax and Wi-Fi
Wireless Fidelity (Wi-Fi) includes three already approved standards IEEE802.11a, b and g. By utilizing the 5.8GHz frequency band, IEEE802.11a is able to deliver 11Mbps of bandwidth. The most resent IEEE802.11g is operating on the 2.4GHz frequency band and is capable of providing 54Mbps bandwidth.2 In comparative, although WiMax’s 75Mbit/s is 21Mbps faster than the most resent and fastest Wi-Fi standard, which represents a 38% increase, but many people consider 38 percent increase in speed is not a big improvement. However, WiMax is targeted to provide user with wireless access to Internet or connectivity among users based on related Internet Protocols. Given the fact that today’s Internet bandwidth for a normal user is less than 5Mbps; 75Mbps will be enough for most users.
To a normal user, if he is inside the coverage of both Wi-Fi and WiMax, he might notice that connection with WiMax has faster and more stable responses (Lower ping time), especially with the presence of other users. This is because WiMax uses an algorithm that allocates an adjustable window time to each user. The allocation algorithm is stable even when the station is over-subscribed. Unlike in the Wi-Fi scenario, all users will compete for the chance to talk and they will be selected in a random manner. The adjustable window time also provide Internet Service Providers (ISPs) new opportunities. ISPs will able to tailor-cut the speed it offers to its customers according to their needs. ISPs may offer packages that compete on the low end with reduced speed at very low price, or they can bring ultra-fast connections to pro users at premium. In terms of the user capacity, WiMax supports much many more users than Wi-Fi. We can see that, although the speed for each user similar, but WiMax’s biggest advantage is it can support more users.
Compare WiMax and GPRS
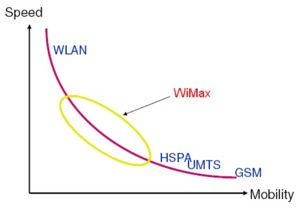
Since WiMax products can also be used on mobile phone devices to provide data accesses, this report will also compare WiMax with the data transmission over the General Packet Radio Service Network (GPRS) that are currently used by almost all mobile service providers. Similar to WiMax, the already existing GPRS network covers a wide area but is able to provide 160Kbps data rate to its user. This is much less than WiMax’s 75Mbps. Moreover, data transmission for GPRS is only able to achieve 30-80 Kbps in practice. The diagram below shows the speed advantage of WiMax over many other data transmission technology used on cell phone.
High bandwidth available means more creative applications for the user. One example is a group of business workers having a video conference call over their WiMax enabled phones. With a faster connection speed, users will be able to enjoy clear voice from other participants and higher quality videos. Voice over IP is another hot topic for WiMax. Since each mobile phone device will have stable high-speed connection to Internet, users can make phone calls over Internet to avoid the extra long distance and roaming charges. The third trend is related to the latest trend of merging multimedia player and mobile phone. According to Vodafone Japan, music and video downloads are the number one usage of Internet connections from mobile devices. With the fast connection speed, content providers can certainly bring their current service to the next level. Imagine watching TV programs or movies on demand from your mobile phones or purchase new songs and play it with phones with a few clicks. In conclusion, WiMax is able to bring more bandwidth to the mobile devices and other content providers, application developers will deliver more and more services to benefit the end user.
Reference
1. Worldwide Interoperability for Microwave Access Forum. WiMAX Overview. March 26, 2007
2. Marshall, Brian (2006). How WiFi Works.
See Also
Bluetooth Technology
802.11 Wireless Security
Personal Area Networks(PAN)
WiFi Security
Networking with House Wiring
External Links
WiMax: A Tutorial at tutorialsweb
WiMax at Wikipedia
WiMax Forum
Contributor
Xuan Li
Last Update
Mar. 27, 2007